Quickstart
This tutorial will showcases how to use Axon to build a Spiking Neural Network (SNN) that can multiply two signed decimal numbers. In particular, it covers how to use a multiplication SNN module available in Axon, how input values to it, how simulate its execution, and how to read out and interpret the output.
Multiplier and encoder
The spiking neural networks (SNN) defined with Axon SDK are slightly different from what’s conventionally understood by spiking neural networks (for example, in ML). They have two fundamental differences:
- Axon’s SNNs don’t need to be trained.
- Axon uses a pair of spikes to encode an individual value.
The Axon SDK provides an already-made library of computational modules. These are SNNs implementing a specific and deterministic computation.
One of such modules is a multiplication network:
from axon_sdk.networks import MultiplierNetwork

Axon abstracts the complexity of the underlying SNNs into a modular interface that allows composing computation kernels to achieve larger operations.
The multiplier network requires an encoder to work. The encoder is the component that translates between arithmetic values and spike intervals.
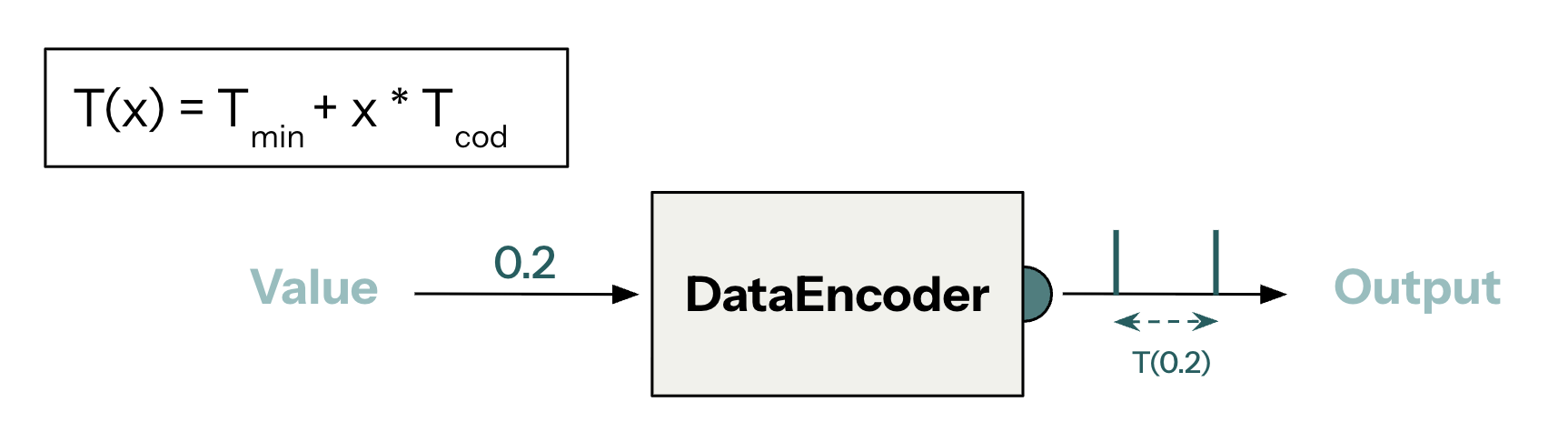
from axon_sdk.primitives import DataEncoder
encoder = DataEncoder(Tmin=10.0, Tcod=100.0)
spikes = enc.encode_value(0.2)
interval = spikes[1] - spikes[0]
value = enc.decode_interval(interval)
spikes
>> (0, 30.0)
value
>> 0.2
Simulating the SNN
There is one last fundamental ingredient to execute the SNN - the simulator:
from axon_sdk.primitives import Simulator
sim = Simulator(multiplier_net, encoder, dt=0.01)
The simulator runs a sequential execution of the dynamics of the SNN, hence the need of a simulation timestep parameter (dt).
The simulator also allows to input values to the network. Under the hood, it uses the encoder to do so:
sim.apply_input_value(0.5, neuron=net.input1)
sim.apply_input_value(0.5, neuron=net.input2)
The last step is to run the simulation and to readout the spikes emitted by the output neuron
sim.simulate(simulation_time=400)
spikes = sim.spike_log.get(net.output.uid, [])
interval = spikes[1] - spikes[0]
output_val = encoder.decode_interval(interval)
output_val
>> 0.2
Instead of using spiking rates to encode values which encode values over many spikes, Axon uses inter-spike intervals. The delay betweekn a couple of spikes encodes a value. This makes Axon extremely spike sparse, hence optimizing for energy consumption (when deploying spiking neural networks to hardware, processing each spike has an energy cost)